Rheological investigation of collagen, fibrinogen, and thrombin solutions for drop-on-demand 3D bioprinting†
Abstract
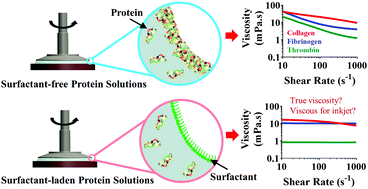
Collagen, fibrinogen, and thrombin proteins in aqueous buffer solutions are widely used as precursors of natural biopolymers in three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting applications. The proteins are sourced from animals and their quality may vary from batch to batch, inducing differences in the rheological properties of such solutions. In this work, we investigate the rheological response of collagen, fibrinogen, and thrombin protein solutions in bulk and at the solution/air interface. Interfacial rheological measurements show that fibrous collagen, fibrinogen and globular thrombin proteins adsorb and aggregate at the solution/air interface, forming a viscoelastic solid film at the interface. The viscoelastic film corrupts the bulk rheological measurements in rotational rheometers by contributing to an apparent yield stress, which increases the apparent bulk viscosity up to shear rates as high as 1000 s−1. The addition of a non-ionic surfactant, such as polysorbate 80 (PS80) in small amounts between 0.001 and 0.1 v/v%, prevents the formation of the interfacial layer, allowing the estimation of true bulk viscosity of the solutions. The estimation of viscosity not only helps in identifying those protein solutions that are potentially printable with drop-on-demand (DOD) inkjet printing but also detects inconsistencies in flow behavior among the batches.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Soft Matter Most Popular 2020


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...