Magnetism in bimetallic PtxNiN−x clusters via cross-atomic coupling†
Abstract
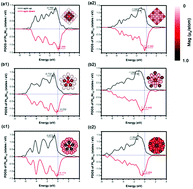
Bimetallic PtxNiN−x clusters exhibit notable magnetization as demonstrated by many previous experiments. However, the origin of magnetic properties of the bimetallic PtxNiN−x clusters and the effects of morphology, composition, size, and chemical order on the magnetic properties are still not fully understood. In this work, we performed a systematic study on the electronic and magnetic properties of three model magic-number clusters, PtxNiN−x (N = 13, 55, and 147). Each bimetallic cluster was designed with prototypical symmetric morphologies, i.e., cuboctahedron (CUBO), decahedron (DEC), and icosahedron (ICO). Four distinct chemical orders were also implemented for each bimetallic cluster, namely, core–shell, onion-ring, L10-ordered, and crown. Detailed computations of the charge and magnetic moment distributions show that the magnetic Ni atoms can transfer electrons to the surrounding layers of Pt atoms in the PtxNiN−x clusters, which then induces a magnetic moment onto the nearest two layers of non-magnetic Pt atoms. Among the PtxNiN−x clusters considered, the cluster with the crown chemical ordering in the ICO morphology possesses the highest magnetic moment. Our comprehensive studies not only offer an explanation for the origin of magnetic properties in the PtxNiN−x clusters, but also provide guidance for future design and synthesis of bimetallic clusters with optimal magnetic properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...