Carrier transport manipulation for efficiency enhancement in blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices with a 4,4′-bis(N-carbazolyl)-2,2′-biphenyl host†
Abstract
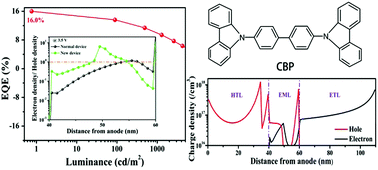
4,4′-N,N′-Dicarbazol-biphenyl (CBP) is a common host in phosphorescent organic light emitting devices (PhOLEDs). However, it is rarely used to fabricate blue PhOLEDs due to its lower triplet energy level. Here, a 53.8% enhancement of the maximum external quantum efficiency (EQEmax) from CBP-based blue PhOLEDs by introducing a carrier adjustment layer (CAL) is reported. A EQEmax of 16.0% is achieved in blue PhOLEDs with a CAL using CBP:bis[(4,6-difluorophenyl)pyridinato-N,C2′](picolinato)iridium(III) (FIrpic) as an emitting layer (EML). This efficiency is the highest record of CBP-based blue PhOLEDs, and it is comparable to most blue PhOLEDs which use a single host with a high triplet energy level. The efficiency enhancement is attributed to the balanced transport and distribution of electrons and holes in the EML. The results suggest that the effect of a more balanced distribution of carriers in the EML on the efficiency of blue PhOLEDs is comparable to the triplet energy level of the host materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...