A fluorescent probe for simultaneously sensing NTR and hNQO1 and distinguishing cancer cells†
Abstract
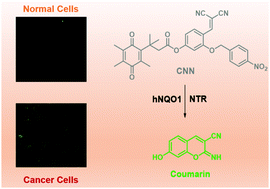
Identifying cancer at the cellular level during an early stage offers the hope of greatly improved outcomes for cancer patients. As potential cancer biomarkers, nitroreductase (NTR) and human quinine oxidoreductase 1 (hNQO1) are overexpressed in many type of cancer cells. Simultaneous detection of these two biomarkers would benefit diagnostic precision in related cancers without yielding false positive results. Herein, based on a dye generated in situ strategy, a dual-enzyme-responsive probe, CNN, was rationally designed and synthesized by installing p-nitrobenzene and trimethyl-locked quinone propionic acid groups, which are specific for NTR and hNQO1, respectively, into a single fluorophore. This probe is only activated in the presence of both NTR and hNQO1 and produces a large fluorescence response, enabling the detection of both endogenous NTR and hNQO1 activity in living cells. The imaging results indicate that the CNN probe differentiates cancer cells (HeLa, MDA-MB-231 and HepG2 cells) from normal liver HL-7702 cells owing to the existence of relatively high endogenous levels of both biomarkers in these cancer cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...