Molten ionic oxides for CO2 capture at medium to high temperatures†
Abstract
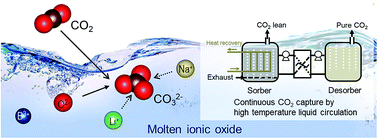
The development of efficient low cost CO2 capture systems is a critical challenge for mitigating climate change while meeting global energy demand. Herein, we demonstrate the first liquid absorbents for CO2 capture at medium to high temperatures (500 to 700 °C). Molten ionic oxides based on sodium borate and the mixed alkali-metal borates show remarkably fast kinetics and intrinsic regenerability, with no observable deterioration in performance over multiple absorption–desorption cycles under both temperature- and pressure-swing operations. The behavior of the molten ionic oxides is ascribed to the instantaneous formation of carbonate ions in the molten oxides without the diffusional transport restrictions imposed by solid product layers characteristic of solid adsorbents. The new liquid absorbents will enable continuous processing and thermal integration via a simple absorber–desorber arrangement, thereby overcoming the challenges previously restraining high temperature CO2 capture and opening up new opportunities in clean energy production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...