Multifunctional bipyramid-Au@ZnO core–shell nanoparticles as a cathode buffer layer for efficient non-fullerene inverted polymer solar cells with improved near-infrared photoresponse†
Abstract
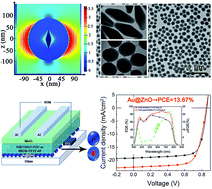
How to enhance the light absorption of the photoactive layer with a limited thickness is still a big challenge. To take advantage of the plasmonic effects of sharp-edged metal nanoparticles and the excellent electron collection ability of ZnO in polymer solar cells (PSCs), we designed and synthesized multifunctional bipyramid-Au@ZnO core–shell nanoparticles (Au@ZnO). These materials were integrated into inverted non-fullerene PSCs with a limited photoactive layer thickness. We conducted electron mobility, dissociation probability, and time-resolved photoluminescence testing. Our results were supported by the theoretical prediction that the Au@ZnO is capable of boosting the near-infrared photo-response and effectively extracting the electrons from the photoactive layer. These features markedly improved carrier transport and enabled fast charge transfer to the electrode. Promising power conversion efficiency (PCE) values of 10.88% and 13.67% were achieved for the PBDTBDD:ITIC and PBDB-TF:IT-4F-based PSCs with a Au@ZnO cathode buffer layer (CBL). This performance was superior to that of reference devices without a Au@ZnO CBL, which showed PCEs of only 9.09% and 11.86%, respectively. Our findings suggest great potential for the design of a multifunctional CBL with good electron extraction and plasmonic properties for high performance PSCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...