Dissolution of concentrated surfactant solutions: from microscopy imaging to rheological measurements through numerical simulations†
Abstract
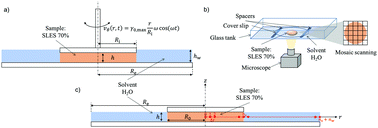
Concentrated aqueous solutions of surfactants, often referred to as pastes, experience complex phase and rheology changes upon dissolution in water, which is a typical step in the production of liquid detergents. During the dilution process, depending on water content, surfactant molecules can arrange in different morphologies, such as lamellar or cubic and hexagonal structures. These phases are characterized by different physico-chemical properties, such as viscosity or diffusivity, which lead to non-simple transport mechanisms during the dissolution process. In this work, we investigate the dissolution of concentrated Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulfate (SLES) pastes in water under quiescent conditions by coupling different experimental techniques. A thorough rheological characterization of the system showed non-monotonic changes of several orders of magnitude in its viscosity and viscoelastic moduli as a function of water content. Time-lapse microscopy allowed us to image the dynamic evolution of the phase changes as water penetrated in a disk-shaped sample (with the same geometry used in rheological tests). Numerical simulation, based on a simple diffusion-based multi-parameter model is shown to describe satisfactorily SLES dissolution data.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...