Synthesis and appraisal of a hydroxyapatite/pectin hybrid material for zinc removal from water†
Abstract
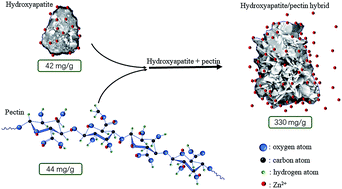
A simple method to modify hydroxyapatite and pectin into an efficient zinc sorbent was investigated. Process and formulation modifications enabled the formation of a flower-like hydroxyapatite/pectin hybrid material. The hybrid material was characterized with scanning electron microscopy, elemental analysis, and zeta potential tests. Sorption data were analyzed with different kinetic and isotherm models. The results showed that the pseudo-second order kinetic model and two-staged isotherm curves with Langmuir at the first stage and a Freundlich model the at second stage could best describe the zinc sorption on the hybrid. The maximum experimental sorption capacity was 330.4 mg Zn2+ per gram of sorbent, which was obtained with an initial concentration of 260 mg L−1 Zn2+ at pH 5.0. pH monitoring and Zeta potential tests suggested surface complexation and electrostatic attraction were fundamental in the zinc sorption process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...