Enhanced catalytic activity of Au core Pd shell Pt cluster trimetallic nanorods for CO2 reduction†
Abstract
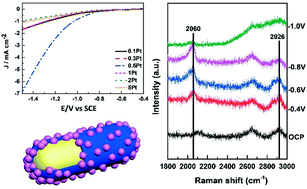
Herein, Au core Pd shell Pt cluster nanorods (Au@Pd@Pt NRs) with enhanced catalytic activity were rationally designed for carbon dioxide (CO2) reduction. The surface composition and Pd–Pt ratios significantly influenced the catalytic activity, and the optimized structure had only a half-monolayer equivalent of Pt (θPt = 0.5) with 2 monolayers of Pd, which could enhance the catalytic activity for CO2 reduction by 6 fold as compared to the Pt surface at −1.5 V vs. SCE. A further increase in the loading of Pt actually reduced the catalytic activity; this inferred that a synergistic effect existed among the three different nanostructure components. Furthermore, these Au NRs could be employed to improve the photoelectrocatalytic activity by 30% at −1.5 V due to the surface plasmon resonance. An in situ SERS investigation inferred that the Au@Pd@Pt NRs (θPt = 0.5) were less likely to be poisoned by CO because of the Pd–Pt bimetal edge sites; due to this reason, the proposed structure exhibited highest catalytic activity. These results play an important role in the mechanistic studies of CO2 reduction and offer a new way to design new materials for the conversion of CO2 to liquid fuels.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editors' collection: Carbon Dioxide Capture/Reduction


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...