A smart tumor-microenvironment responsive nanoprobe for highly selective and efficient combination therapy†
Abstract
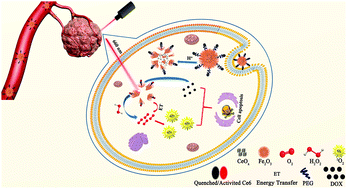
The therapeutic effects of chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy (PDT) are limited seriously by tumor hypoxia and low cell uptake capacity. Herein, a smart tumor-microenvironment (TME) responsive nanoprobe was developed using pH-responsive and decomposed CeOx/Fe2O3 as a carrier not only to strengthen cell uptake capacity, increase drug packaging efficiency and modulate tumor hypoxia, but also to act as an acceptor of Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and achieve energy quenching of an excited photosensitizer. Due to the urchin-like hollow structures of the CeOx/Fe2O3 carrier, the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin (DOX) and the photosensitizer chlorine e6 (Ce6) could be co-loaded to form the nanoprobe CeOx/Fe2O3-C&D. In normal tissue, the nanoprobe CeOx/Fe2O3-C&D showed weak cytotoxicity. Once in the TME, the CeOx/Fe2O3 nanoshells began to break up, DOX was released rapidly at the tumor site, and CeOx/Fe2O3 showed catalase-like activity to decompose endogenous H2O2 and produce O2 persistently to overcome hypoxia in situ. Meanwhile the Ce6 was transformed from a “silent state” to an “activated state”, generating the fluorescence signal and singlet oxygen (1O2) by weakening the FRET efficiency. Therefore, our study showcases an innovative strategy to enhance cell uptake capacity, adjust tumor hypoxia and achieve highly selective and specific combination therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...