Visible light photocatalytic water oxidation over complex perovskites Sr3BNb2O9 (B = Mg, Ca and Sr) doped with nitrogen†
Abstract
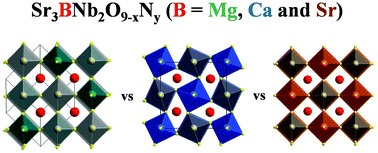
Nitrogen doping has been frequently adopted as a useful strategy to endow wide band gap semiconductors with visible light photocatalytic activities. Nevertheless, factors that may influence the effects of nitrogen doping are seldom touched. In this work, we synthesized a series of complex perovskites Sr3BNb2O9 (B = Mg, Ca and Sr) and applied nitrogen doping strategies to these compounds. Our results suggest that a wealth of important parameters such as structural distortions, cation ordering, nitrogen uptake, visible light absorption and surface hydrophilicity are all strongly correlated with cations in the B site. Accommodating large Sr cations in the B site helps to reduce structural distortions and the level of cation ordering. It is also helpful to increase nitrogen uptake, visible light absorption and surface hydrophilicity, all of which seem to be responsible for a much higher photocatalytic activity for water oxidation reactions. The strong correlations between B site cations and the aforementioned parameters open a new avenue for the design and development of efficient photocatalytic properties of these promising materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...