Dicyclohexylurea derivatives of amino acids as dye absorbent organogels and anion sensors†
Abstract
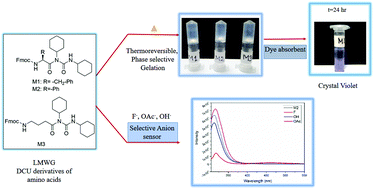
Dicyclohexyl urea (DCU) derivatives of amino acids Fmoc-Phe-DCU (M1), Fmoc-Phg-DCU (M2) and Fmoc-Gaba-DCU (M3) have been shown to form phase selective, thermoreversible and mechanically robust gels in a large range of organic solvents. This is the first report of low molecular weight gelators (LMWG) from DCU derivatives of amino acids. The self-assembly mechanism of the organogels has been probed using concentration dependent 1H NMR, DMSO titration 1H NMR, fluorescence, FTIR, PXRD and FESEM techniques. Self-assembly leading to gelation process is mainly driven by hydrophobicity and π–π stacking interactions in between Fmoc groups. Interestingly, the gels can absorb several kinds of organic dyes efficiently and can be reused for dye absorption for multiple cycles. Additionally, M1–M3 act as sensors for anions like fluoride, acetate and hydroxide, for which they have specific fluorescence response. Gel formation by M1–M3 is completely arrested in the presence of fluoride. The possible binding mode of fluoride has been delineated using DFT studies. Calculations suggest, involvement of urea NH in a six membered intramolecular hydrogen bond, rendering it unavailable for fluoride binding. Backbone –NH of the amino acids of M1–M3 is responsible for fluoride binding. The reported small, economically viable, synthetically facile molecules not only enrich the repertoire of LMWG molecules, but can have multifaceted applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Supramolecular chemistry in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...