Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) as a probe for detection of charge-transfer between TiO2 and CdS nanoparticles†
Abstract
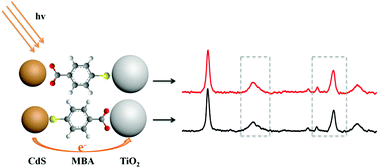
Charge-transfer processes of coupled semiconductor nanoparticles play an essential role in many application fields of semiconductors. It has been difficult to characterize the charge-transfer process between two semiconductor nanoparticles. Herein, we propose a new analytical tool with the chemical mechanism of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) to provide information about the charge-transfer process in coupled semiconductor nanoparticle systems. In this work, two assemblies (namely, TiO2–MBA–CdS and CdS–MBA–TiO2) have been fabricated as models to explore the charge-transfer process between TiO2 and CdS nanoparticles by SERS. 4-MBA works as both the linker of these two semiconductors and the probe of SERS to reveal the charge-transfer process. Under excitations at 633 and 785 nm, which are far from the surface plasmon resonance of the CdS and TiO2 nanoparticles in the assemblies, there are some obvious changes in the peak intensities and peak shifts in the SERS spectra after introducing CdS to the TiO2/MBA system and TiO2 to the CdS/MBA system. The differences of the peak intensities in the TiO2–MBA–CdS and CdS–MBA–TiO2 assemblies show different charge-transfer processes. We have found that the dipole moment of a MBA molecule greatly influences the charge-transfer process between the TiO2 and CdS nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...