Discovery of (aza)indole derivatives as novel respiratory syncytial virus fusion inhibitors
Abstract
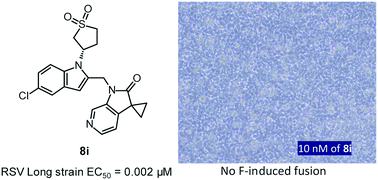
A new class of indole derivatives (3) have been identified as potent RSV fusion inhibitors. SAR exploration revealed that 5-Cl and the sulfonyl side chain of the indole scaffold are crucial for anti-RSV activity. Further optimization led to the discovery of a cyclic sulfone (8i) with 2 nM anti-RSV activity and a much improved PK profile compared to the non-cyclic sulfone counterpart.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...