Controlling cellular distribution of drugs with permeability modifying moieties†
Abstract
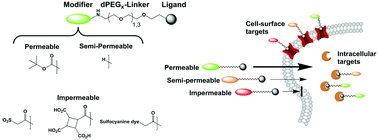
Phenotypic screening provides compounds with very limited target cellular localization data. In order to select the most appropriate target identification methods, determining if a compound acts at the cell-surface or intracellularly can be very valuable. In addition, controlling cell-permeability of targeted therapeutics such as antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) and targeted nanoparticle formulations can reduce toxicity from extracellular release of drug in undesired tissues or direct activity in bystander cells. By incorporating highly polar, anionic moieties via short polyethylene glycol linkers into compounds with known intracellular, and cell-surface targets, we have been able to correlate the cellular activity of compounds with their subcellular site of action. For compounds with nuclear (Brd, PARP) or cytosolic (dasatinib, NAMPT) targets, addition of the permeability modifying group (small sulfonic acid, polycarboxylic acid, or a polysulfonated fluorescent dye) results in near complete loss of biological activity in cell-based assays. For cell-surface targets (H3, 5HT1A, β2AR) significant activity was maintained for all conjugates, but the results were more nuanced in that the modifiers impacted binding/activity of the resulting conjugates. Taken together, these results demonstrate that small anionic compounds can be used to control cell-permeability independent of on-target activity and should find utility in guiding target deconvolution studies and controlling drug distribution of targeted therapeutics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Molecular Pharmacology


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...