Efficient synthesis of enantiopure amines from alcohols using resting E. coli cells and ammonia†
Abstract
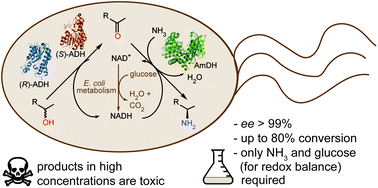
α-Chiral amines are pivotal building blocks for chemical manufacturing. Stereoselective amination of alcohols is receiving increased interest due to its higher atom-efficiency and overall improved environmental footprint compared with other chemocatalytic and biocatalytic methods. We previously developed a hydrogen-borrowing amination by combining an alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) with an amine dehydrogenase (AmDH) in vitro. Herein, we implemented the ADH-AmDH bioamination in resting Escherichia coli cells for the first time. Different genetic constructs were created and tested in order to obtain balanced expression levels of the dehydrogenase enzymes in E. coli. Using the optimized constructs, the influence of several parameters towards the productivity of the system were investigated such as the intracellular NAD+/NADH redox balance, the cell loading, the survival rate of recombinant E. coli cells, the possible toxicity of the components of the reaction at different concentrations and the influence of different substrates and cosolvents. In particular, the cofactor redox-balance for the bioamination was maintained by the addition of moderate and precise amounts of glucose. Higher concentrations of certain amine products resulted in toxicity and cell death, which could be alleviated by the addition of a co-solvent. Notably, amine formation was consistent using several independently grown E. coli batches. The optimized E. coli/ADH-AmDH strains produced enantiopure amines from the alcohols with up to 80% conversion and a molar productivity up to 15 mM. Practical applicability was demonstrated in a gram-scale biotransformation. In summary, the present E. coli-ADH-AmDH system represents an important advancement towards the development of ‘green’, efficient and selective biocatalytic processes for the amination of alcohols.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...