Highly efficient epoxidation of vegetable oils catalyzed by a manganese complex with hydrogen peroxide and acetic acid
Abstract
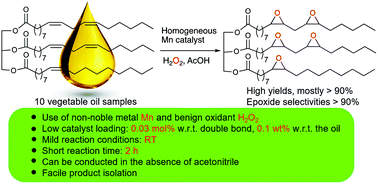
Epoxidized vegetable oils (EVOs) are versatile building blocks for lubricants, plasticizers, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) stabilizers, and surface coating formulations. In this paper, a catalytic protocol for the efficient epoxidation of vegetable oils is presented that is based on a combination of a manganese catalyst, H2O2 as an oxidant, and acetic acid as an additive. This protocol relies on the use of a homogeneous catalyst based on the non-noble metal manganese in combination with a racemic mixture of the N,N′-bis(2-picolyl)-2,2′-bispyrrolidine ligand (rac-BPBP). The optimized reaction conditions entail only 0.03 mol% of the manganese catalyst with respect to the number of double bonds (ca. 0.1 wt% with respect to the oil) and ambient temperature. This epoxidation protocol is highly efficient, since it allows most of the investigated vegetable oils, including cheap waste cooking oil, to be fully epoxidized to EVOs in more than 90% yield with excellent epoxide selectivities (>90%) within 2 h of reaction time. In addition, the protocol takes place in a biphasic reaction medium constituted by the vegetable oil itself and an aqueous acetic acid phase, from which the epoxidized product can be easily separated via simple extraction. In terms of efficiency and reaction conditions, the current epoxidation protocol outperforms previously reported catalytic protocols for plant oil epoxidation, representing a promising alternative method for EVO production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...