Effect of germination time on antioxidative activity and composition of yellow pea soluble free and polar soluble bound phenolic compounds
Abstract
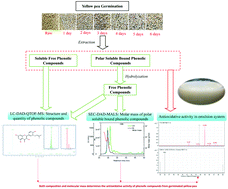
This research aims to study antioxidative activities of polar solvent extractable phenolic compounds from yellow peas with different germination times against oil-in-water emulsion oxidation. After germination (0, 2, 4, and 6 days), soluble free and polar soluble bound phenolic compounds were extracted and their antioxidative activity was evaluated using stripped soybean oil (SSO)-in-water emulsions. Liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-QTOF-MS) and size-exclusion chromatography with multiangle-light-scattering and refractive-index detection (SEC-MALS-RI) were employed to analyze the phenolic composition and molar mass, respectively. Antioxidative activities of soluble free phenolic compounds increased in the SSO-in-water emulsion system, while those of polar soluble bound phenolic compounds decreased with germination. On the basis of chemometric analysis, pratensein (2), phloridzin (4), quercetin (9), sayanedine (12), hesperetin (13), glyzaglabrin (14), and pinocembrin (15) were speculated as the pivotal phenolic compounds responsible for the hydrogen donating capacity. Additionally, decreased molecular weight of soluble bound phenolic compounds was accompanied by the reduction of antioxidative activity in SSO-in-water emulsions indicating that the moieties of polar soluble bound phenolic compounds also have an important impact on the antioxidative activity of phenolic compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
