Waste activated sludge disintegration by hydroxyl and sulfate radical-based oxidation: a comparative study†
Abstract
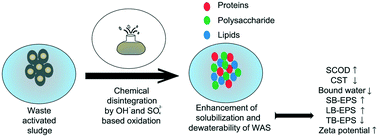
This study comparatively investigated hydroxyl and sulfate radical-based oxidation processes for the first time to enhance the disintegration degree (DD) and dewaterability of waste activated sludge (WAS). Hydrogen peroxide (HP), calcium hypochlorite (CHC), peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and peroxydisulfate (PDS) were selected as the oxidants in this study. Response surface methodology (RSM) and Box–Behnken design (BBD) were used to determine the operational parameters (oxidant dosage: 0.5–2 mmol g−1 TSS; initial pH: 2–4 for HP treatment, 2–10 for other treatments; Fe2+ to oxidant ratio: 0.5–2) at the first stage of the experiments. According to these multivariate analyses, high correlation coefficients (R2 > 95.27%) were obtained for each treatment, and the DD values of the sludge in terms of soluble COD were found to be 5.39%, 8.86%, 9.40% and 6.03% for HP, CHC, PMS and PDS treatment under optimum conditions, respectively The DD of WAS was also evaluated in terms of the concentrations of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and total dissolved nitrogen (TDN) under the optimum conditions, and higher DDDOC (16.65%) and DDTDN (15.46%) values were obtained in the CHC treatment. The types and concentrations of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) were also investigated under the optimum conditions, and it was found that proteins (PN) and polysaccharides (PS) increased in the soluble EPS (SB-EPS) and loosely-bound EPS (LB-EPS), while both components decreased in the tightly-bound EPS (TB-EPS) in almost all treatments. Further experiments were performed to evaluate the temperature effect on disintegration and dewaterability of WAS, and it was found that the increase of temperature from 30 to 60 °C enhanced the DD and the reduction of the capillary suction time (CST) of the sludge samples. In terms of WAS dewaterability, a higher CST reduction was obtained in the HP treatment. The results of this study showed that higher DD and CST reduction values were achieved with hydroxyl-based oxidants, and these treatments could be used successfully in pretreatment of WAS.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...