Photocatalyst with a metal-free electron–hole pair double transfer mechanism for pharmaceutical and personal care product degradation†
Abstract
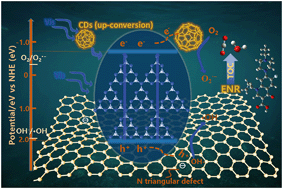
Advanced photocatalytic oxidation processes for water purification have been the subject of extensive research over the past several years; however, the low efficiency utilization of photogenerated carriers remains a major challenge. To optimize the performance of photocatalysts, we initially synthesized carbon dots (CDs) and boron nitride (BN), which were employed as photoelectron and photohole transfer receptors, respectively. These were compounded with graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) to form a high-efficiency ternary photocatalytic material (CDs/g-C3N4/BN (CCN)) that possessed the double transfer characteristics of photogenerated carriers. This metal-free composite exhibited improved activity, which was ∼5 times higher than pristine g-C3N4 for the degradation of enrofloxacin under blue LED irradiation. Moreover, these hybrid photocatalysts demonstrated good reusability. According to property–photoactivity correlation analysis, the CDs and BN manifested their ability for enhancing the production of reactive oxygen species by boosting the transfer of charge carriers. Our work revealed the synergistic transfer of photogenerated electron–hole pairs to expand the use of photocatalysts, while providing a new perspective for their synthesis and development to further enrich the discipline of material design.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...