Ion effects on molecular interaction between graphene oxide and organic molecules
Abstract
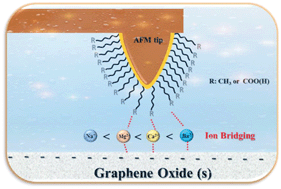
Interactions between graphene oxide (GO) and organic molecules play a role in processes such as environmental remediation and water treatment. However, little is known about underlying molecular level processes with the presence of ions. In this study, we utilized atomic force microscopy (AFM) in chemical force mapping (CFM) mode to directly probe their adhesion interactions. AFM tips were functionalised to serve as models for nonpolar and polar organic molecules, i.e. with alkyl, –CH3, and carboxyl, –COO(H). For experiments with –COO(H) tips, adhesion between GO and tips decreased in the order: Ba2+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Na+, whereas for the –CH3 tips, ion dependent adhesion was relatively low but followed the same: Ba2+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ ≈ Na+. Calculations with Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek (DLVO) theory and the Schulze–Hardy rule could not account for the observations. We propose that ion bridging plays a definitive role in adhesion between –COO(H) tips and the GO surface. This is consistent with proposed models with density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Adhesion of –CH3 tips is a response to the hydrophilic interactions and the ion dependent part is suggested to arise from ion bridging between slightly negative charged –CH3 tips and the GO surface. High pH had a notable influence on the adhesion of the –COO(H) tip but a negligible effect on the –CH3 tip. These results offer important insights into interactions between solutions and mineral surfaces with adsorbed organic molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...