Effect of perimeter interface length between 2D WO3 monolayer domain and γ-Al2O3 on selective hydrogenolysis of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol†
Abstract
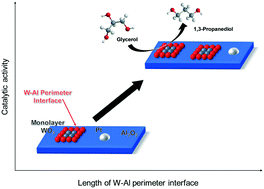
The relationship between the structure of W species on Pt/WO3/Al2O3 catalysts and their activity for selective hydrogenolysis of glycerol to 1,3-propanediol was investigated. Structural analysis by spectroscopic techniques including X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray adsorption fine structure (XAFS) revealed the formation of two-dimensional WO3 monolayer domains on the surface of γ-Al2O3 at a WO3 loading level of below 20 wt%. Evaluation of the reduction properties of W species by H2 temperature programed reduction (TPR) suggested the presence of two kinds of W species with different reduction properties loaded on γ-Al2O3, and W species at the edge of a WO3 domain was reduced more easily than that inside of a WO3 domain. Furthermore, the length of the perimeter interface between a two-dimensional WO3 monolayer domain and γ-Al2O3 (W–Al perimeter interface) could be estimated from the difference in their reducibility. The positive correlation between W–Al perimeter interface length and the yield of 1,3-propanediol in hydrogenolysis of glycerol indicated that a W–(OH)–Al site at the W–Al perimeter interface functioned as a main active site.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...