Effects of water on the stochastic motions of propane confined in MCM-41-S pores†
Abstract
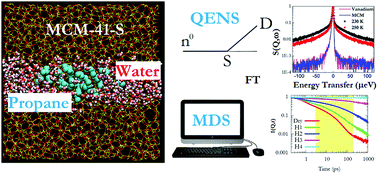
Hydrocarbons confined in porous media find applications in a wide variety of industries and therefore their diffusive behavior is widely studied. Most of the porous media found in natural environments are laden with water, which might affect the confined hydrocarbons. To quantify the effect of hydration, we report here a combined quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation study on the dynamics of propane confined in the 1.5 nm-wide micropores of MCM-41-S in the presence of water at 230 and 250 K. To eliminate the strong incoherent signal from water and emphasize the propane signal we have used heavy water (D2O). QENS data show two dynamically different populations of propane in MCM-41-S and suggest that the presence of water hinders the diffusion of propane. Weak elastic contributions to the QENS spectra suggest that only long-range translational motion of propane molecules contributes to the quasielastic broadening. MD simulations carried out using a model cylindrical silica pore of 1.6 nm diameter filled with water and propane agree with the experimental finding of water hindering the diffusion of propane. Further, the simulation results suggest that the slowing down of propane motions is a function of the water content within the pore and is stronger at higher water contents. At high water content, the structure and the dynamics, both translational and rotational, of propane are severely impacted. Simulation data suggest that the rotational motion of the propane molecule occurs on time scales much faster than those accessible with the QENS instrument used, and thus explain the weak elastic contribution to the QENS spectra measured in the experiments. This study shows the effects of hydration on the structure and dynamics of volatiles in porous media, which are of interest for fundamental understanding and applied studies of confined fluids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...