Angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy as applied to X-ray mirrors: an in depth study of Mo/Si multilayer systems
Abstract
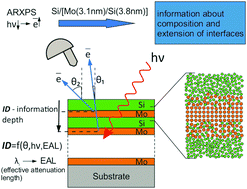
We present an approach adapted to study the interface (composition and extension) of X-ray multilayer mirrors using angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARXPS). In the approach we rely on the concept of the average effective attenuation length (EAL) of the photoelectron and not on the inelastic mean free path (IMPF), which allows us to take into account the contribution of elastically scattered electrons and to increase the accuracy of the determined thickness of the layers. We apply the developed approach to study the formation of interfaces in a multilayer periodic Mo/Si mirror. The chemical composition and significance of the interfaces depending on the number of periods were investigated by means of the ARXPS spectra decomposition technique. Formation of a molybdenum silicide MoSi2 at the interfaces was revealed. It was shown that molybdenum silicide with different thicknesses is formed at the interfaces depending on the film order. In addition, it was established that increasing the period number of the [Mo/Si] system leads to a decrease of the interface extension.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...