Cu(ii)-nanoparticle-derived structures under CO2 reduction conditions: a matter of shape†
Abstract
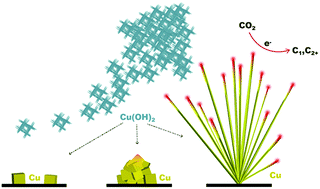
Uncovering the nature and formation mechanisms of active sites in electrocatalysts is crucial for advancing energy conversion technologies. Cu(II)-derived electrodes show unique activity in CO2 electroreduction, but its origins are not fully understood. We investigate the structural evolution of Cu(OH)2 nanoparticle-derived electrodes and its effect on their performance in CO2 electroreduction.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...