Competition of singlet and triplet recombination of radical pairs in photoreactions of carboxy benzophenones and aromatic amino acids†
Abstract
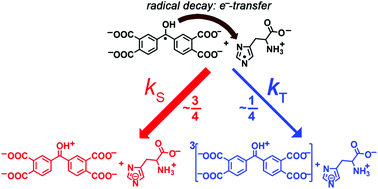
Time-resolved chemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization (CIDNP) and transient absorption (TA) were applied to reveal the branching ratio of the singlet and triplet recombination channels in the reaction of short-lived radicals of carboxy benzophenones and the aromatic amino acids histidine, tryptophan, and tyrosine in neutral aqueous solution. It was established that the share of triplet recombination increases with increasing number of carboxylic groups: no triplet recombination was found for 4-carboxy benzophenone, whereas ∼13% of radicals of 4,4′-dicarboxy benzophenone (DCBP) and ∼27% of radicals of 3,3′,4,4′-tetracarboxy benzophenone (TCBP) react with histidine radicals from the triplet state of radical pairs. The main idea is that the protonated (π,π*) triplet state of TCBP or DCBP is populated via back electron transfer from the ketyl radical of TCBP or DCBP to the radical of the amino acid. The protonated triplet state of the ketone decays with the formation of a metastable hydroxylated product, which is detected by TA. Taking into account triplet recombination provides excellent coincidence between experimental data and the simulated CIDNP kinetics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...