Atomically thin NiB6 monolayer: a robust Dirac material†
Abstract
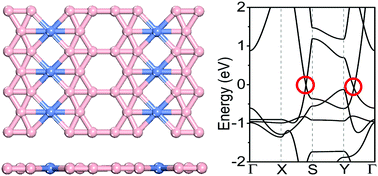
Two-dimensional (2D) Dirac materials have attracted extensive research interest due to their high carrier mobility and ballistic charge transport, and they hold great promise for next-generation nanoscale devices. Here, we report a computational discovery of a stable 2D Dirac material, an NiB6 monolayer, which is identified by an extensive structure search, and its dynamic and thermal stabilities are confirmed by phonon and ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) simulations. This monolayer structure possesses anisotropic elastic properties with a Young's modulus of 189 N m−1, which is higher than that of phosphorene or silicene. Electronic band calculations reveal a double Dirac cone feature near the Fermi level with a high Fermi velocity of 8.5 × 105 m s−1, and the results are robust against external strains. We also propose two possible synthesis approaches based on a stable Ni4B8+ precursor or by embedding Ni atoms into the δ4 boron framework. The present findings offer a strong physics basis for the design and synthesis of a novel 2D Dirac material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...