π-Hydrogen bonding and aromaticity: a systematic interplay study
Abstract
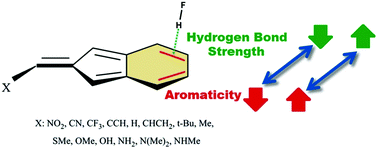
Quantum DFT calculations, corrected for long-range interactions, have been carried out on complex models formed between HF as a proton donor and 2-methylene-2H-indene derivatives as proton acceptors. Using various exocyclic X substitutions, mutual effects of the aromaticity and the strength of the resulting π-hydrogen bond (after its evaluation by AIM methodology) have been investigated. The results show that the aromaticity of 6-membered rings and the hydrogen bond strength increase upon increasing the electron-donating character of the X-substituents. Based on some aromaticity indices (HOMA, FLU, SA and NICS(1)zz), it has been shown that the formation of a π-hydrogen bond causes an increase of aromaticity of the 6-membered ring. Also, the strength of the resulting π-hydrogen bond (with an energy of about 4.0 to 7.0 kcal mol−1) depends on the aromaticity of the 6-membered ring and increases with an increase in the aromaticity. In addition, a linear relationship was found between the most negative value of the molecular electrostatic potential (Vmin) and the HOMA, which confirms that the Vmin in the region of the studied ring could be used as a new index to estimate the amount of aromaticity. The electronic properties of the complexes have also been evaluated by means of the molecular electrostatic potential (MEP), the atoms in molecules (AIM) and the natural bond orbital (NBO) analyses.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...