Carbon nanotube-encapsulated cobalt for oxygen reduction: integration of space confinement and N-doping†
Abstract
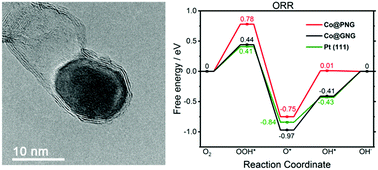
We report carbon nanotube-encapsulated cobalt as an efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalyst (onset potential of 0.94 V and half-potential of 0.84 V). Calculation results firstly reveal that Co protected by graphitic-N-doped carbon holds more negative charge (−1.22 eV) and has an energy barrier (0.56 eV) lower than that of pyridinic-N-doped carbon (−1.11 eV; 0.78 eV), which is responsible for the ORR activity. The corresponding Zn–air batteries deliver an excellent gravimetric energy density of 837 W h kg−1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...