Heptylmannose-functionalized cellulose for the binding and specific detection of pathogenic E. coli†
Abstract
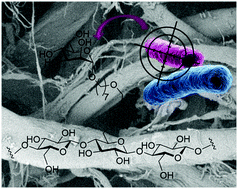
We developed a chemical method to covalently functionalize cellulose nanofibers and cellulose paper with mannoside ligands displaying a strong affinity for the FimH adhesin from pathogenic E. coli strains. Mannose-grafted cellulose proved efficient to selectively bind FimH lectin and discriminate pathogenic E. coli strains from non-pathogenic ones. These modified papers are valuable tools for diagnosing infections promoted by E. coli, such as cystitis or inflammatory bowel diseases, and the concept may be applicable to other life-threatening pathogens.
- This article is part of the themed collection: ChemComm: Editor’s Choice


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...