N-Doped carbon nanofibers derived from bacterial cellulose as an excellent metal-free catalyst for selective oxidation of arylalkanes†
Abstract
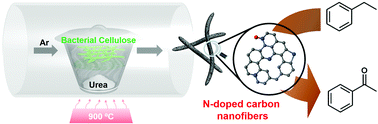
N-Doped carbon nanofibers derived from one-step pyrolysis of low-cost bacterial cellulose with the assistance of urea were reported. Owing to their interconnected nanofibrous structure and high specific surface area as well as high N doping, they exhibited excellent catalytic performance for selective oxidation of arylalkanes even with O2 as an oxidant in aqueous solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...