Detecting the structural assembly pathway of human antimicrobial peptide pores at single-channel level†
Abstract
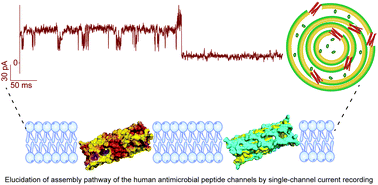
The pore-forming structures of an anionic human antimicrobial peptide dermcidin (DCD) in a membrane environment has not been demonstrated previously. Using single-channel electrical recordings, we characterized the structural and functional properties of the DCD peptide channel in lipid membranes. We show that a 48-residue, 8 nm long anionic DCD-1L peptide is folded in the right conformation in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) that spontaneously inserts into lipid bilayers to form well-defined channels. However, the DCD-1L peptides are not properly folded in n-dodecyl-β-D-maltoside (DDM), resulting in unstable channels suggesting the significance of specific detergent in stable channel formation. Furthermore, a 25-residue cationic DCD SSL-25 peptide formed channels both in SDS and DDM micelles as the length of the peptide matches with the thickness of the membrane. Finally, we quantified the permeation of small molecules through the DCD channels in liposome assays. Accordingly, we propose a molecular model demonstrating the structural self-assembly of the DCD channels in the membrane. We suggest that an understanding of the mechanism of action of DCD peptides at single-channel resolution will lead to developing peptide-based therapeutics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...