Improved detection of group A Streptococcus during thermal contrast amplification vs. visual reading of clinical rapid diagnostic tests†
Abstract
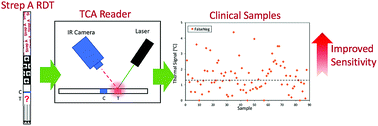
Group A Streptococcus causes significant health care costs and burdens. In the form of a mild infection, streptococcal pharyngitis is difficult to diagnose and manage while having the potential to progress to life-threatening invasive infections. The unsatisfactory performance of rapid diagnostic tests frequently requires follow-up high-sensitivity confirmatory testing, causing additional time and cost. Improving rapid detection sensitivity will lead to more timely and accurate diagnosis. In previous work, we demonstrated that our robust, easy-to-use thermal contrast amplification reader improves traditional rapid diagnostic test strip sensitivity 8-fold by testing dilutions of control solutions. In order to facilitate translation, we now present a clinical study to demonstrate the impact of a thermal contrast amplification reader on strep throat detection. Our results show that the TCA reader identifies over 50% of clinical false negative samples, indicating that the reader could significantly reduce the need for confirmatory strep throat tests in a primary care setting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...