The neutralization of heparan sulfate by heparin-binding copolymer as a potential therapeutic target
Abstract
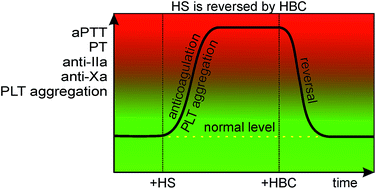
Besides regulating ligand–receptor and cell–cell interactions, heparan sulfate (HS) may participate in the development of many diseases, such as cancer, bacterial or viral infections, and their complications, like bleeding or inflammation. In these cases, the neutralization of HS could be a potential therapeutic target. The heparin-binding copolymer (HBC, PEG41-PMAPTAC53) was previously reported by us as a fully synthetic compound for efficient and safe neutralization of heparins and synthetic anticoagulants. In a search for molecular antagonists of HS, we examined the activity of HBC as an HS inhibitor both in vitro and in vivo and characterized HBC/HS complexes. Using a colorimetric Azure A method, isothermal titration calorimetry and dynamic light scattering techniques we found that HBC binds HS by forming complexes below 200 nm with less than 1 : 1 stoichiometry. We confirmed the HBC inhibitory effect in rats by measuring activated partial thromboplastin time, prothrombin time, anti-factor Xa activity, anti-factor IIa activity, and platelet aggregation. HBC reversed the enhancement of all tested parameters caused by HS demonstrating that cationic synthetic block copolymers may have a therapeutic value in various disorders involving overproduction of HS.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...