Dimethylaniline functionalised pyrene fluorophores; dual colour pH switching in solution and self-assembled monolayers†
Abstract
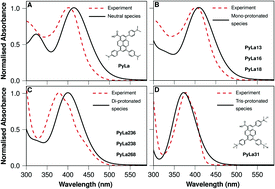
A pyrene charge transfer fluorophore with three ionizable N,N-dimethylaniline moieities was explored as an interfacial pH switch. The parent carboxylate compound and the thiolated derivative were shown by spectroscopy combined with DFT calculation to be successively and reversibly protonated. Protonation leads to progressive decrease of intensity of the 550 nm centered N,N-dimethylaniline to pyrene charge transfer emission which on protonation of the third site, leads to extinction of this transition and evolution of an intense blue (450 nm) pyrene-centered emission. Concomitant loss of the charge transfer absorbance was observed and the changes are reversed on neutralization of pH. A self-assembled monolayer of the thiolated derivative was prepared on gold and found from voltammetry of ferricyanide/ferrocyanide probe to form close packed monolayers. The probe voltammetry, label-free electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of the film was monitored as a function of pH and progressive, but reversible protonation steps were reflected in decreasing film resistance. The Stokes shift of the probe prevents self-quenching so a broad, charge transfer fluorescence centered around 540 nm was recorded for the self-assembled monolayer where as per solution, progressive and reversible reduction in intensity was observed. The facile assembly, impedance and optical switching make these materials potentially interesting as on–off or two colour on–off–on fluorescence switches with potential applications in logic gates or in responsive surface applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...