Effects of sulfate on biotite interfacial reactions under high temperature and high CO2 pressure†
Abstract
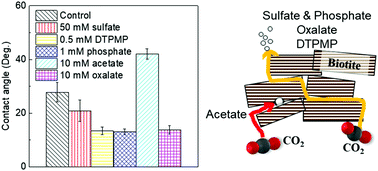
To ensure the safety and efficiency of engineered subsurface operations, it is vital to understand impacts of aqueous chemistries on brine–mineral interactions in subsurface environments. In this study, using biotite as a model phyllosilicate, we investigated the effects of sulfate on its interfacial reactions under subsurface relevant conditions (95 °C and 102 atm of CO2). By making monodentate mononuclear complexes with biotite surface sites, 50 mM sulfate enhanced biotite dissolution by 40% compared to that without sulfate. However, sulfate at lower concentrations than 50 mM did not obviously affect biotite dissolution. In addition, sulfate did not impact secondary mineral precipitation. However, even without any discernible surface morphological change, sulfate adsorption made biotite surfaces more hydrophilic. To provide a more comprehensive perspective on environmentally-abundant ligands, we further comparatively examined the effects of various inorganic (e.g., sulfate and phosphate) and organic ligands (e.g., acetate, oxalate, and phosphonates) on biotite interfacial interactions and assessed their impacts on physico-chemical properties. We found that the presence of phosphate and phosphonates significantly promoted precipitation of Fe- and Al-bearing secondary minerals, but sulfate, acetate, and oxalate did not. Biotite surface wettability was also altered as a result of changes in biotite surface functional groups and surface charges by ligand adsorption: sulfate, oxalate, phosphate, and phosphonate made biotite more hydrophilic, while acetate made it less hydrophilic. This study provides useful new insights into the effects of brine chemistries on brine–mineral interactions, enabling safer and more efficient engineered subsurface operations.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...