Impact of bound ionic defects on the hydration of acceptor-doped proton-conducting perovskites
Abstract
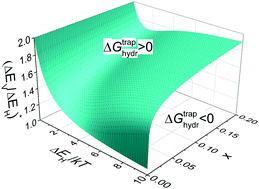
The role of various acceptor-bound states of ionic defects in the defect thermodynamics and hydration of acceptor-doped proton-conducting perovskites is theoretically studied. It is shown that the relation between the trapping energies of protons (ΔEH) and vacancies (ΔEV) bound to acceptor impurities is one of the major factors governing hydration. As the trapping energies ΔEH and ΔEV increase, the proton concentration at not too low temperatures can either increase or decrease depending on the ΔEV/ΔEH ratio. The surface of the boundary values (ΔEV/ΔEH)* separating the regions where trapping enhances or inhibits hydration is determined as a function of the proton trapping energy and dopant content. It is demonstrated that trapping can result in an unusual non-monotonic dependence of the hydration enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energy on dopant content. The distributions of protons and vacancies over bound and free sites are determined for different binding energies of defects, dopant content and external conditions. The contribution of the stable 3-particle complexes of acceptor-bound defects to hydration thermodynamics is shown to be significant provided certain relations for the binding energies of 2- and 3-particle complexes are satisfied. In particular, oxygen vacancies bound by two acceptors can cause deviation of the hydration isobars from their typical behavior and lead, in some cases, to incomplete oxide hydration in experiments. The effect of acceptor-bound defects on hydration and defect thermodynamics is illustrated by the examples of BaZrO3 and BaCeO3 doped with different acceptors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...