Percolation behaviors of ionic and electronic transfers in Li3−2xCoxN†
Abstract
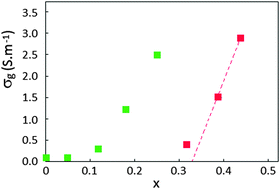
Nitridocobaltates Li3−2xCoxN, with Li3N-type layered structure, are promising compounds as negative electrode materials for Li-ion batteries. In the present paper, we report the first detailed broadband dielectric spectroscopy (BDS) study on lithiated transition metal nitrides. The ionic and electronic conductivities of Li3−2xCox□xN compounds (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.44) are investigated as a function of the concentration x of cobalt ions, cationic vacancies (□) and lithium ions. Dielectric and conductivity spectra were recorded within the frequency range of 60–1010 Hz from 200 to 300 K. Experimental results exhibit two types of electric conduction: the first one is due to lithium ion diffusion (for 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.25) and the second one due to electronic transfers (for x ≥ 0.3). Furthermore, two percolation transitions are evidenced and associated with 3D ionic transfers (threshold at x ≈ 0.11) on the one hand and 2D electronic transfers (threshold at x ≈ 0.30) on the other hand. Upon increasing the frequency, dielectric relaxations appear from larger to smaller sample scales. These successive polarizations appear with increasing frequency in the following order: (a) sample/silver paint interface; (b) particles (aggregates of grains); (c) grains (crystallites); (d) local ionic and electronic motions within the grains. Evolutions of dielectric relaxation parameters (dielectric strength and relaxation frequency) with Co content confirm the two percolation transitions. Surprisingly, the grain conductivity has a large discontinuity immediately below the electronic percolation threshold where any local- and long-range ionic movement disappears without electronic transfer. This discontinuity would be due to a narrow transition from ionic to electronic conduction when x increases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...