Activation of natural halloysite nanotubes by introducing lanthanum oxycarbonate nanoparticles via co-calcination for outstanding phosphate removal†
Abstract
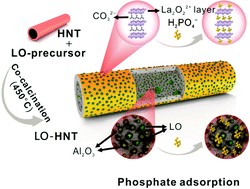
Halloysite nanotubes were activated via co-calcination of halloysite and the precursors of lanthanum oxycarbonate (LO), generating reactive alumina nanoparticles and uniformly anchoring LO nanoparticles to halloysite surfaces. The resulting LO–alumina combination exhibits record-high phosphate adsorption capacity as well as excellence in adsorption selectivity and sewage phosphate removal.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...