Thermochemically stable ceramic composite membranes based on Bi2O3 for oxygen separation with high permeability†
Abstract
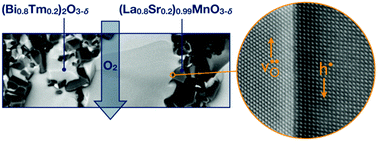
Ceramic oxygen separation membranes can be utilized to reduce CO2 emissions in fossil fuel power generation cycles based on oxy-fuel combustion. State-of-the-art oxygen permeable membranes based on Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ (BSCF) offer high oxygen permeability but suffer from long-term instability, especially in the presence of CO2. In this work, we present a novel ceramic composite membrane consisting of 60 vol% (Bi0.8Tm0.2)2O3−δ (BTM) and 40 vol% (La0.8Sr0.2)0.99MnO3−δ (LSM), which shows not only comparable oxygen permeability to that of BSCF but also outstanding long-term stability. At 900 °C, oxygen fluxes of 1.01 mL min−1 cm−2 and 1.33 mL min−1 cm−2 were obtained for membranes with thicknesses of 1.35 mm and 0.75 mm, respectively. Moreover, significant oxygen fluxes were obtained at temperatures down to 600 °C. A stable operation of the membrane was demonstrated with insignificant changes in the oxygen flux at 750 °C for approx. one month and at 700 °C with 50% CO2 as the sweep gas for more than two weeks.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...