Me–N–C (Me = Fe, Cu, and Co) nanosheet as a promising charge-controlled CO2 capture material†
Abstract
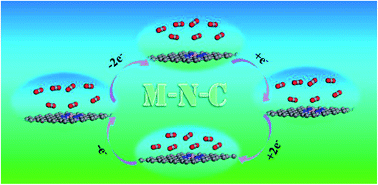
It is necessary to explore advanced materials with high CO2 selectivity and simple CO2 regeneration to weaken the greenhouse effect. Therefore, in this study, we report a comprehensive investigation of CO2, CH4, H2, C2H2, C2H4 and C2H6 on different Me–N–C nanosheets with different charge densities via density functional theory calculations. Our results demonstrate that CO2 is weakly absorbed on neutral and positively charged Me–N–C monolayer, whereas CO2 adsorption strength can be dramatically strengthened on a negatively charged Me–N–C monolayer, especially the Fe–N–C nanosheet. The adsorption energy of CO2 on the negatively charged Fe–N–C nanosheet with a negative charge density of 15.27 × 1013 e− cm−2 is −3.07 eV, which is about 10 times larger than that (−0.283 eV) on neutral one; in addition, it also shows high CO2 selectivity from mixtures containing CH4, H2, C2H2, C2H4 and C2H6. This investigation can provide valuable information for designing feasible adsorbent materials having high CO2 adsorption capacity and selectivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...