A high dielectric constant non-fullerene acceptor for efficient bulk-heterojunction organic solar cells†
Abstract
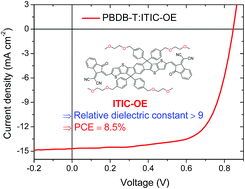
The majority of organic semiconductors have a low relative dielectric constant (εr < 6), which is an important limitation for organic solar cells (OSCs). A high dielectric constant would reduce the exciton binding energy, reduce charge carrier recombination losses, and thereby enhance the overall device performance of OSCs. However, the development of organic/polymeric semiconductors with higher relative dielectric constants (εr > 6) has attracted a very limited attention. Moreover, high performance OSCs based on high dielectric constant photovoltaic materials are still in their infancy. Herein, we report an oligoethylene oxide side chain-containing non-fullerene acceptor (ITIC-OE) with a high relative dielectric constant of εr ≈ 9.4, which is two times larger than that of its alkyl chain-containing counterpart ITIC. Encouragingly, the OSCs based on ITIC-OE show a high power conversion efficiency of 8.5%, which is the highest value for OSCs that employ high dielectric constant materials. Nevertheless, this value is lower than those of ITIC-based control devices. The less phase-separated morphology in blend films due to the reduced crystallinity of ITIC-OE and the too good miscibility between PBDB-T and ITIC-OE are responsible for the lower device performance. This work suggests additional prerequisites to make high dielectric constants play a significant role in OSCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...