Molecular design with silicon core: toward commercially available hole transport materials for high-performance planar p–i–n perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
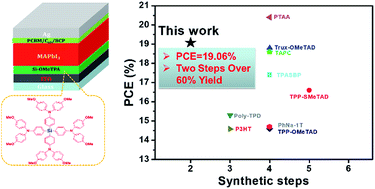
Organic hole transport layers (HTL) play a very important role for realizing high performance and low-cost planar p–i–n perovskite solar cells (pero-SCs). In this work, we synthesized two X-shaped organic HTL materials, Si-OMeTPA and SiTP-OMeTPA, with silicon cores and triphenylamine (TPA) derivative branches. This molecular design strategy can substantially simplify synthetic procedures making them available for reducing device costs. This is particularly applicable for Si-OMeTPA since it can be synthesized by two steps from commercial raw materials showing a total yield of over 60%. This molecularly designed Si-OMeTPA possesses advantages of high thermal stability, high crystallinity with a long range ordered lamellar structure, and excellent hole mobility. The resulting HTL can also facilitate the sequential growth of high-quality perovskite films, giving a significantly enhanced photovoltaic performance with a best power conversion efficiency of 19.06%, which is one of the highest PCE among the planar p–i–n pero-SCs to date. In addition, the devices exhibit negligible hysteresis, good reproducibility, and stability. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first example of an easily synthesized HTL material in planar p–i–n pero-SCs that shows superior performance relative to the well-known poly(bis(4-phenyl)(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)amine) (PTAA) HTL.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...