Heterobimetallic metal–organic framework nanocages as highly efficient catalysts for CO2 conversion under mild conditions†
Abstract
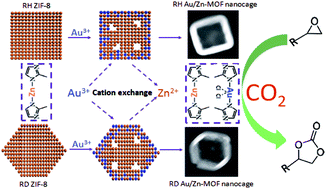
It is of critical importance to design and fabricate highly active and stable catalysts for CO2 conversion. Herein, we synthesize a kind of novel porous heterobimetallic catalyst by manipulating the structural evolution of metal–organic framework (MOF) nanocrystals. The starting material, homometallic ZIF-8 nanoparticles, transforms in solution by cation exchange with Au3+ ions into heterobimetallic Au/Zn-MOF nanocages that favor the enhancement of active sites. With the use of regular hexahedral (RH) ZIF-8 and rhombic dodecahedral (RD) ZIF-8 nanoparticles as the templates, we obtain RH and RD Au/Zn-MOF nanocages with controllable shell thickness, respectively. The resulting Au/Zn-MOF nanocages are employed to catalyze the cycloaddition of CO2 and epoxides under mild reaction conditions. The excellent catalytic performance is demonstrated by high yields of 95–99% along with easy recyclability of the Au/Zn-MOF nanocages, which outperform most of the reported MOF-based catalysts and a homogeneous Au catalyst due to the synergetic effect of the two metallic components and the unique hollow structures. Impressively, these Au/Zn-MOF nanocages exhibit remarkable catalytic activity for CO2 conversion even at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. These nanomaterials thus hold great promise as catalysts for CO2 conversion in terms of facile preparation, abundant multiple active sites, and enhanced catalytic activity and stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...