Neuroprotective effect of total glycosides from paeonies against neurotoxicity induced by strychnos alkaloids related to recovering the levels of neurotransmitters and neuroendocrine hormones in rat serum and brain†
Abstract
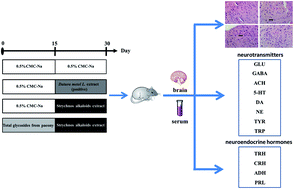
Semen Strychni, a classical traditional Chinese medicine, has been widely used for its anti-tumor, analgesic and anti-inflammatory angiogenesis effects. However, taking an overdose of Semen Strychni might result in extreme neurotoxicity. Strychnos alkaloids are the main toxic constituents of Semen Strychni. Total glycosides from paeonies are considered to have neuroprotective effects. In this study, twelve potential endogenous biomarkers in rat serum and brain were monitored to investigate the protective effect of total glycosides from the paeony against strychnos alkaloids-induced neurotoxicity. A sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method was developed and validated to monitor eight neurotransmitters including glutamate, γ-aminobutyric acid, acetylcholine serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, tryptophan and tyrosine. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method was selected for determination of four neuroendocrine hormones including thyrotrophin-releasing hormone, corticotrophin-releasing hormone, antidiuretic hormone and prolactin. Results showed that continuous administration of strychnos alkaloids for 15 days caused significant changed levels of the biomarkers (especially the four neuroendocrine hormones). Meanwhile, total glycosides from paeony pretreated rats (administrated with total glycosides from the paeony for 15 days before exposure to strychnos alkaloids) showed recovered levels of these biomarkers. The results suggested that the neurotransmitters and neuroendocrine hormones in serum and brain might play potential roles as biomarkers. This study provides the possibility of alleviating the Semen Strychni-induced neurotoxicity in clinic by pre-protection with total glycosides from paeonies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...