Phosphate adsorption onto thermally dehydrated aluminate cement granules
Abstract
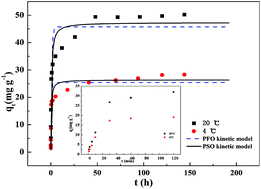
Phosphorus is the main element for eutrophication of water bodies. Aluminate cement is a cheap building material rich in aluminium and calcium which have significant effects on phosphate adsorption. This study aimed at the investigation of removal behavior of phosphate by thermally dehydrated aluminate cement granules, treated at different temperatures, and the adsorption mechanisms. It was found that 600 °C was the optimal temperature, producing excellent granules with a particle size of 0.6–1.5 mm (T600), giving a great adsorption capacity of phosphate of 49.1 mg P per g and presenting fast and high initial adsorption, reaching a capacity of 23.7 mg P per g within 30 min at 20 °C. The phosphate adsorption process was dominated by chemical adsorption, mainly through inner-sphere complexion and phosphate precipitation on the surface of the adsorbent. Compared with other phosphate adsorbents, T600 may be an economical and efficient adsorbent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...