High magnetoresistance in ultra-thin two-dimensional Cr-based MXenes†
Abstract
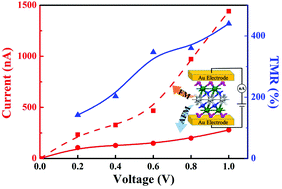
Developing effective magnetoresistance devices has become beneficial due to their extensive applications in electronics such as data storage. One challenge is to reduce the scale of devices while maintaining a high magnetoresistance. Another challenge for the applications of magnetoresistance devices involves synthesizing them with stable interfaces. Antiferromagnetic Cr-based MXenes are similar to tunneling magnetoresistance junctions, and can be synthesized in a straightforward manner. Density functional theory calculations show that the medium adhesion strength between Au electrodes and Cr-based MXene can ensure the formation of stable interfaces. Exchange coupling between Cr atoms in different atomic layers is found to decrease to 0.4 meV with increasing thickness. Magnetoresistance values are higher than 400% with 1.0 V. The results show that Cr-based MXenes are promising magnetoresistance devices with high magnetoresistance values and ultra-thin layers (about 1 nm) and exhibit tunable exchange coupling between Cr atoms through thickness control.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...