Adsorptive removal of p-nitrophenol from water with mechano-synthesized porous organic polymers†
Abstract
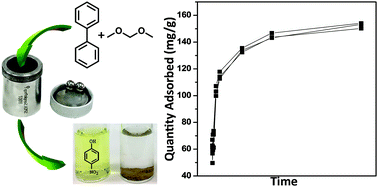
In this work, we demonstrated the successful synthesis of porous organic polymers via a ball-milling procedure. Several readily available benzene derivatives were selected to be polymerized through a Friedel–Crafts reaction with FeCl3 as the Lewis acid catalyst and formaldehyde dimethyl acetal as the crosslinker. All the mechano-synthesized porous organic polymers (MPOPs) are not soluble in common organic solvents, and the calculated surface area was over 500 m2 g−1 when biphenyl was used as the monomer. One of the advantages of applying ball-milling in targeted polymer synthesis is bypassing the use of large quantity of hazardous chlorinated solvents, which are commonly used in traditional Friedel–Crafts reactions. Considering the aromatic skeleton and hydrophobic nature of these polymers, their performance in p-nitrophenol (PNP) adsorption from water was investigated. The quantification was carried out on an Ionics 3Q 320 LC-MS/MS system with 4-nitrocatechol (PNC) as an internal standard. MPOP-1 and MPOP-3 showed the maximum adsorption capacity of 133.10 and 155.51 mg g−1 for PNP, respectively. Their adsorption kinetics were studied and both adsorption isotherms were well delineated with a pseudo-second-order equation, indicating the availability of strong adsorption sites in both MPOPs for interacting with PNP.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...