The NiGa-LDH@NiWO4 nanocomposite as an electrode material for pseudocapacitors
Abstract
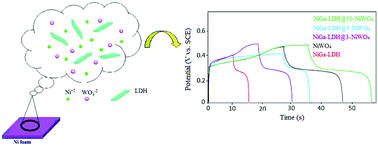
NiGa-LDH@X-NiWO4 (X: 3, 5 or 10 wt% NiWO4) nanocomposites were prepared at room temperature under mild conditions. The synthesized nanocomposites were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) techniques. Electrochemical tests of the nanocomposites were performed by using cyclic voltammetry (CV), galvanostatic charge–discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) techniques. Application of the nanocomposites in a three-electrode cell revealed that the specific capacitance of the NiGa-LDH@10-NiWO4 nanocomposite, i.e. 275 F g−1 at 1 A g−1 current density in pseudocapacitors, is greater than those of the NiGa-LDH@3-NiWO4 and NiGa-LDH@5-NiWO4 nanocomposites and their pure NiGa-LDH and NiWO4 components. Moreover, the NiGa-LDH@10-NiWO4 nanocomposite exhibited a low resistance against ion diffusion and an outstanding capacitive behavior by retaining about 92% of its initial capacitance after performing 1000 cycles at 2 A g−1 current density. The improvement observed in the performance of the fabricated pseudocapacitor can be attributed to the synergistic effects of the NiWO4 and NiGa-LDH materials. Evaluation of the effect of electrolyte alkalinity and the presence of different cations indicated that highly alkaline electrolytes promote the electrochemical behaviour of nanocomposite coated electrodes. Application of the NiGa-LDH@10-NiWO4 electrode, along with an activated carbon electrode, for the fabrication of an asymmetric cell leads to the provision of an excellent cycle life, with 7.11 W h kg−1 energy density and 12 800 W kg−1 power density. Therefore, NiGa-LDH@10-NiWO4 can be considered as a suitable new electrode material used for the fabrication of portable electronics and electric vehicles that rely on high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...