Metal oxide nanoparticle-functionalized sebacic acid-grafted PHEAM nanocarriers for enriched activity of metronidazole against food borne bacteria: in vitro and in vivo study†
Abstract
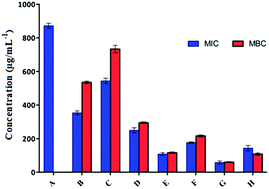
Food borne infection is a serious complication caused by Listeria monocytogenes (L. monocytogenes), a dangerous bacteria. Antibiotics are among the remedies for the destruction of bacterial infection by predominantly targeting the bacterial cell, minimizing the side effects and overcoming antibiotic resistance. In the present study, we have developed non-toxic, biocompatible metal oxide (zinc oxide (ZnO) and magnesium oxide (MgO)) nanoparticle-functionalized sebacic acid-grafted poly(2-hydroxy ethyl methacrylate) (SA-g-PHEMA) with encapsulation of metronidazole (MTZ) antibiotic drug. Nearly 99% of drug encapsulation was obtained. The drug-releasing properties were investigated at different pH, namely, 1.2, 2.5, 5.5 and 7.4 and maximum drug release was attained at acidic pH (5.5). Functionality changes, surface modification, elemental analysis and plane orientation were investigated using FTIR, SEM, TEM, EDX and XRD spectroscopy. Lower MIC value of MgO–ZnO/SA-g-PHEMA–MTZ nanocarrier showed higher antibacterial activity. Furthermore, 79% of biofilm inhibition was obtained against MgO–ZnO/SA-g-PHEMA–MTZ in L. monocytogenes. Colony-forming unit (CFU) assay indicated that the MgO–ZnO/SA-g-PHEMA–MTZ nanocarrier highly reduced the bacterial colonization on the C. elegans worm.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...